Decision Points
Decision points allow our flowchart to branch in multiple directions, and the condition in the decision point determines which branch we follow. All branches must eventually converge and lead to the flowchart's end terminator.
Symbols
A diamond shape represents a decision or branching point. The text in this symbol states the condition, which must usually be true or false. Each branch coming from this symbol is labelled with the result that would cause the program to follow that branch (again, usually true and false).
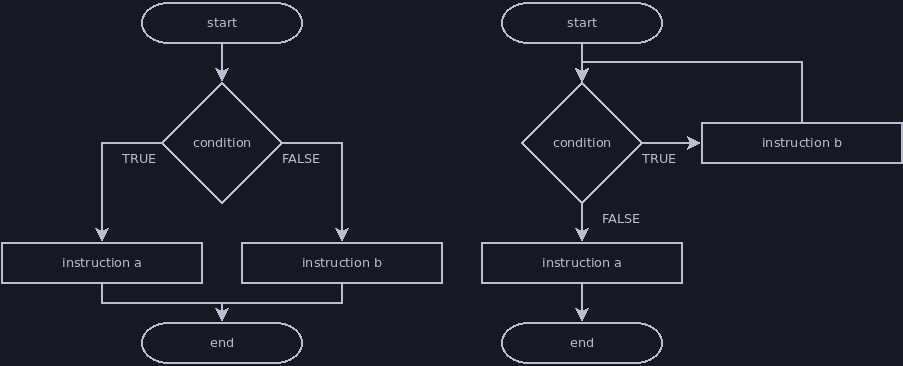
Selection vs Iteration
There are two ways we can use decision points: selection and iteration.
- Selection: the decision point chooses which instruction(s) to perform next, but these do not lead back to earlier parts of the flowchart and converge before the end terminator.
- Iteration: the decision point chooses whether to follow a branch that leads back to an earlier part of the flowchart or to continue towards the end of the flowchart. Iteration allows us to repeat instructions multiple times until a condition is met.
In Java code, selection is handled with if statements and switch statements. Iteration is handled with loops (while, do-while, for).
Selection Examples
The flowcharts below demonstrate selection. The equivalent jshell scripts are also shown after each flowchart.
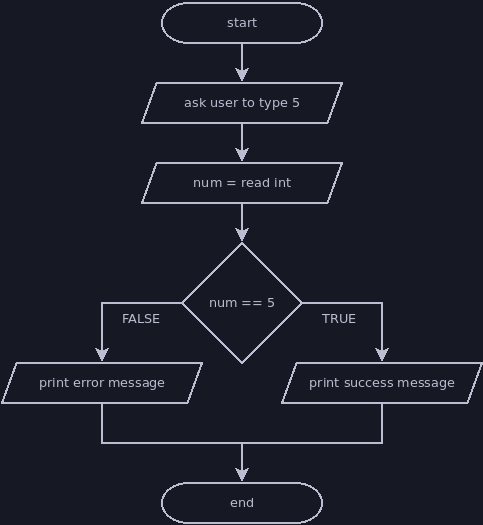
println("Please type the number 5.")
int five = nextInt()
if (five == 5) {
println("Thank you for typing 5.")
} else {
println("Error: you didn't type 5.")
}
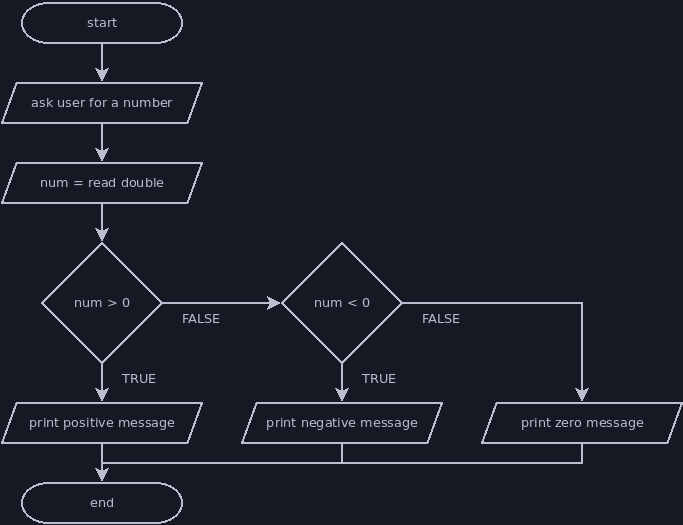
println("Please enter a number.")
int num = nextDouble()
if (num > 0) {
println(num + " is a positive number.")
} else {
if (num < 0) {
println(num + " is a negative number.")
} else {
println(num + " is zero, which is neither positive nor negative.")
}
}
Iteration Examples
The flowcharts below demonstrate iteration. The equivalent jshell scripts are also shown after each flowchart.
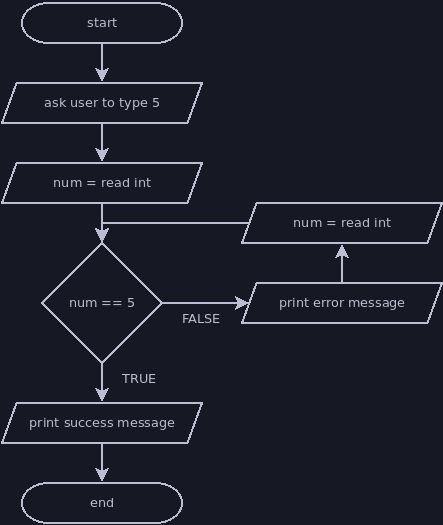
This flowchart duplicates an instruction to more closely match the structure of the jshell code below.
println("Please type the number 5.")
int five = nextInt()
while (five != 5) {
println("Error: you didn't type 5. Try again.")
five = nextInt()
}
println("Thank you for typing 5.")
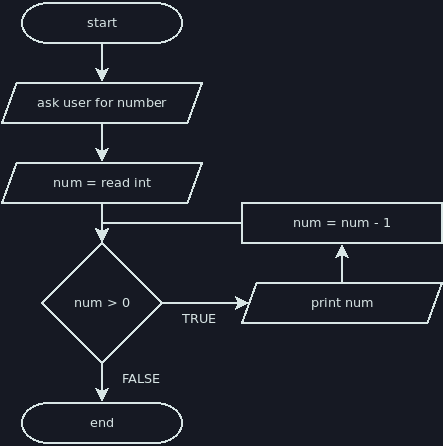
println("Please type a positive integer.")
int countdown = nextInt()
while (countdown > 0) {
println(countdown + "!")
--countdown
}